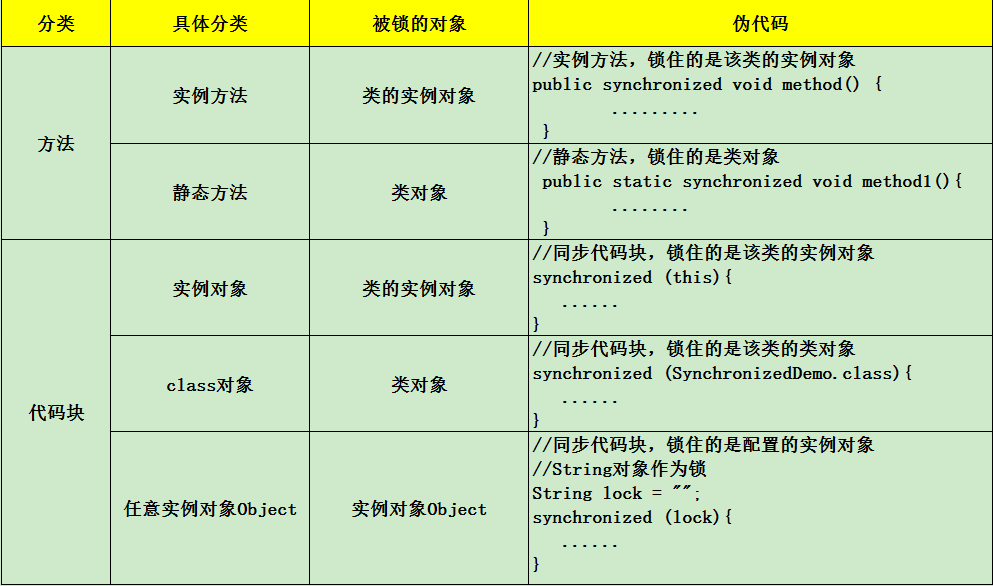
1、在类的实例方法上加synchronized,或者在类的实例对象中加入synchronized (this) {},此时锁住的是该类的实例对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42
| public class TestSynchronized { public synchronized void minus() { int count = 5; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { count--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -> " + count); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } } public void minus2() { synchronized (this) { int count = 5; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { count--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -> " + count); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } } } public synchronized void blockMethod() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + "coming"); } public synchronized static void staticBlockMethod() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + "coming"); } public void unblockMethod() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + "coming"); } }
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
| class TestMain { public static void main(String[]args){ TestSynchronized tt = new TestSynchronized(); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { tt.minus(); } },"t1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { tt.minus(); } },"t2"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
|
//执行结果
t1 -> 4
t1 -> 3
t1 -> 2
t1 -> 1
t1 -> 0
t2 -> 4
t2 -> 3
t2 -> 2
t2 -> 1
t2 -> 0
可以看出,因为Thread的Runnable对象是同一个,synchronized很好的锁住了类的实例对象,两个线程同时启动的时候,当一个线程持有锁的时候,另一个对象是不能访问该实例的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
| class TestMain { public static void main(String[]args){ TestSynchronized tt = new TestSynchronized(); Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { tt.minus(); } },"t1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { tt.blockMethod(); } },"t2"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
|
t1 -> 4
t1 -> 3
t1 -> 2
t1 -> 1
t1 -> 0
t2 coming
当t1线程访问类对象的时候,因为blockMethod方法有synchronized关键字,所以t2在t1持有类对象的时候不能访问blockMethod。
将上述tt.blockMethod();换成tt.unblockMethod(); 执行结果如下
t2 coming
t1 -> 4
t1 -> 3
t1 -> 2
t1 -> 1
t1 -> 0
可以看出,有线程持有实例对象,其他线程访问有synchronized的实例方法会阻塞,而访问普通的实例方法不会被阻塞。
2、在类的静态方法上加synchronized,或者加上synchronized (TestSynchronized.class) {},此时锁住的是该类的类对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44
| public class TestSynchronized { public synchronized static void minus() { int count = 5; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { count--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -> " + count); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } } public static void minus2() { synchronized (TestSynchronized.class) { int count = 5; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { count--; System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " -> " + count); try { Thread.sleep(500); } catch (InterruptedException e) { } } } } public synchronized void blockMethod() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + "coming"); } public synchronized static void staticBlockMethod() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + "coming"); } public void unblockMethod() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + "coming"); } public void staticUnblockMethod() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " " + "coming"); } }
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
| class TestMain { public static void main(String[]args){ Thread t1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { TestSynchronized.minus(); } },"t1"); Thread t2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { TestSynchronized.minus(); } },"t2"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } }
|
t1 -> 4
t1 -> 3
t1 -> 2
t1 -> 1
t1 -> 0
t2 -> 4
t2 -> 3
t2 -> 2
t2 -> 1
t2 -> 0
静态方法锁住的是类对象。修改测试方法,如下
- t1调用synchronized的static方法,t2也调用有synchronized的static方法会阻塞。
- t1调用synchronized的static方法,t2调用非synchronized的static方法不会阻塞。
- t1调用synchronized的static方法,t2调用实例的有synchronized的static方法不会阻塞。
- t1调用synchronized的static方法,t2调用实例的非synchronized的static方法不会阻塞。
总结
A. 无论synchronized关键字加在方法上还是对象上,如果它作用的对象是非静态的,则它取得的锁是对象;如果synchronized作用的对象是一个静态方法或一个类,则它取得的锁是对类,该类所有的对象同一把锁。
B. 每个对象只有一个锁(lock)与之相关联,谁拿到这个锁谁就可以运行它所控制的那段代码。
